No products in the cart.
Bandit is a tool designed to find common security issues in Python code. To do this Bandit processes each file, builds an AST from it, and runs appropriate plugins against the AST nodes. Once Bandit has finished scanning all the files it generates a report.
Bandit was originally developed within the OpenStack Security Project and later rehomed to PyCQA.
Installation
Bandit is distributed on PyPI. The best way to install it is with pip:
Create a virtual environment (optional):
virtualenv bandit-env
# Or if you're working with a Python 3 project
python3 -m venv bandit-env
# And activate it:
source bandit-env/bin/activate
Install Bandit:
pip install bandit
# Or if you're working with a Python 3 project
pip3 install bandit
Run Bandit:
bandit -r path/to/your/code
Bandit can also be installed from source. To do so, download the source tarball from PyPI, then install it:
python setup.py install
Usage
Example usage across a code tree:
bandit -r ~/your_repos/project
Example usage across the examples/ directory, showing three lines of context and only reporting on the high-severity issues:
bandit examples/*.py -n 3 -lll
Bandit can be run with profiles. To run Bandit against the examples directory using only the plugins listed in the ShellInjection profile:
bandit examples/*.py -p ShellInjection
Bandit also supports passing lines of code to scan using standard input. To run Bandit with standard input:
cat examples/imports.py | bandit -
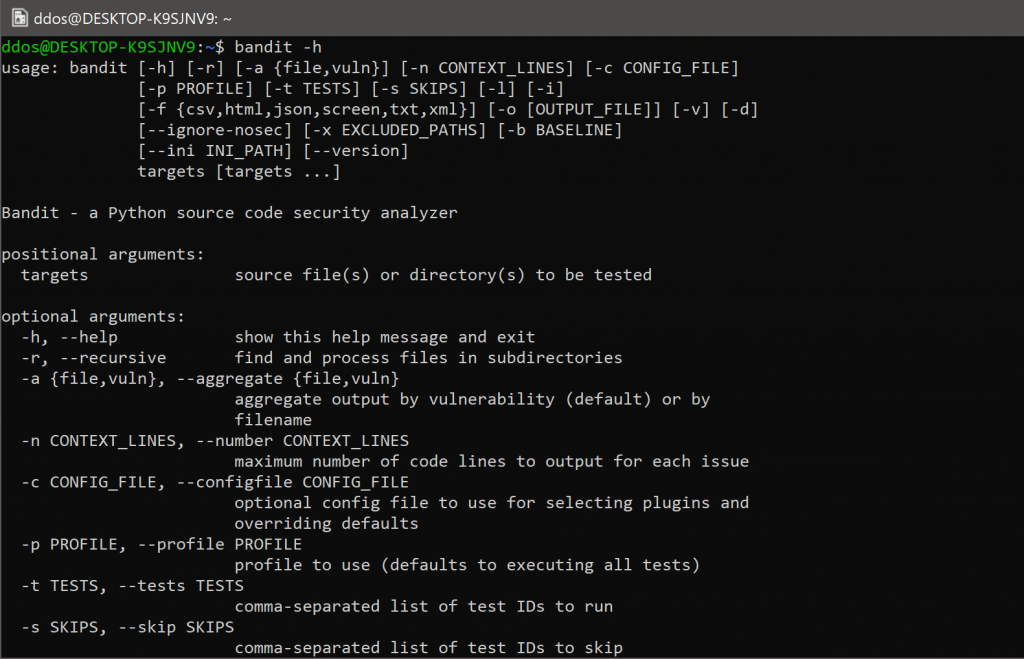
Usage:
$ bandit -h
usage: bandit [-h] [-r] [-a {file,vuln}] [-n CONTEXT_LINES] [-c CONFIG_FILE]
[-p PROFILE] [-t TESTS] [-s SKIPS] [-l] [-i]
[-f {csv,custom,html,json,screen,txt,xml,yaml}]
[--msg-template MSG_TEMPLATE] [-o [OUTPUT_FILE]] [-v] [-d] [-q]
[--ignore-nosec] [-x EXCLUDED_PATHS] [-b BASELINE]
[--ini INI_PATH] [--exit-zero] [--version]
[targets [targets ...]]
Bandit - a Python source code security analyzer
positional arguments:
targets source file(s) or directory(s) to be tested
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-r, --recursive find and process files in subdirectories
-a {file,vuln}, --aggregate {file,vuln}
aggregate output by vulnerability (default) or by
filename
-n CONTEXT_LINES, --number CONTEXT_LINES
maximum number of code lines to output for each issue
-c CONFIG_FILE, --configfile CONFIG_FILE
optional config file to use for selecting plugins and
overriding defaults
-p PROFILE, --profile PROFILE
profile to use (defaults to executing all tests)
-t TESTS, --tests TESTS
comma-separated list of test IDs to run
-s SKIPS, --skip SKIPS
comma-separated list of test IDs to skip
-l, --level report only issues of a given severity level or higher
(-l for LOW, -ll for MEDIUM, -lll for HIGH)
-i, --confidence report only issues of a given confidence level or
higher (-i for LOW, -ii for MEDIUM, -iii for HIGH)
-f {csv,custom,html,json,screen,txt,xml,yaml}, --format {csv,custom,html,json,screen,txt,xml,yaml}
specify output format
--msg-template MSG_TEMPLATE
specify output message template (only usable with
--format custom), see CUSTOM FORMAT section for list
of available values
-o [OUTPUT_FILE], --output [OUTPUT_FILE]
write report to filename
-v, --verbose output extra information like excluded and included
files
-d, --debug turn on debug mode
-q, --quiet, --silent
only show output in the case of an error
--ignore-nosec do not skip lines with # nosec comments
-x EXCLUDED_PATHS, --exclude EXCLUDED_PATHS
comma-separated list of paths (glob patterns
supported) to exclude from scan (note that these are
in addition to the excluded paths provided in the
config file) (default:
.svn,CVS,.bzr,.hg,.git,__pycache__,.tox,.eggs,*.egg)
-b BASELINE, --baseline BASELINE
path of a baseline report to compare against (only
JSON-formatted files are accepted)
--ini INI_PATH path to a .bandit file that supplies command line
arguments
--exit-zero exit with 0, even with results found
--version show program's version number and exit
CUSTOM FORMATTING
-----------------
Available tags:
{abspath}, {relpath}, {line}, {test_id},
{severity}, {msg}, {confidence}, {range}
Example usage:
Default template:
bandit -r examples/ --format custom --msg-template \
"{abspath}:{line}: {test_id}[bandit]: {severity}: {msg}"
Provides same output as:
bandit -r examples/ --format custom
Tags can also be formatted in python string.format() style:
bandit -r examples/ --format custom --msg-template \
"{relpath:20.20s}: {line:03}: {test_id:^8}: DEFECT: {msg:>20}"
See python documentation for more information about formatting style:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html
The following tests were discovered and loaded:
-----------------------------------------------
B101 assert_used
B102 exec_used
B103 set_bad_file_permissions
B104 hardcoded_bind_all_interfaces
B105 hardcoded_password_string
B106 hardcoded_password_funcarg
B107 hardcoded_password_default
B108 hardcoded_tmp_directory
B110 try_except_pass
B112 try_except_continue
B201 flask_debug_true
B301 pickle
B302 marshal
B303 md5
B304 ciphers
B305 cipher_modes
B306 mktemp_q
B307 eval
B308 mark_safe
B309 httpsconnection
B310 urllib_urlopen
B311 random
B312 telnetlib
B313 xml_bad_cElementTree
B314 xml_bad_ElementTree
B315 xml_bad_expatreader
B316 xml_bad_expatbuilder
B317 xml_bad_sax
B318 xml_bad_minidom
B319 xml_bad_pulldom
B320 xml_bad_etree
B321 ftplib
B322 input
B323 unverified_context
B324 hashlib_new_insecure_functions
B325 tempnam
B401 import_telnetlib
B402 import_ftplib
B403 import_pickle
B404 import_subprocess
B405 import_xml_etree
B406 import_xml_sax
B407 import_xml_expat
B408 import_xml_minidom
B409 import_xml_pulldom
B410 import_lxml
B411 import_xmlrpclib
B412 import_httpoxy
B413 import_pycrypto
B501 request_with_no_cert_validation
B502 ssl_with_bad_version
B503 ssl_with_bad_defaults
B504 ssl_with_no_version
B505 weak_cryptographic_key
B506 yaml_load
B507 ssh_no_host_key_verification
B601 paramiko_calls
B602 subprocess_popen_with_shell_equals_true
B603 subprocess_without_shell_equals_true
B604 any_other_function_with_shell_equals_true
B605 start_process_with_a_shell
B606 start_process_with_no_shell
B607 start_process_with_partial_path
B608 hardcoded_sql_expressions
B609 linux_commands_wildcard_injection
B610 django_extra_used
B611 django_rawsql_used
B701 jinja2_autoescape_false
B702 use_of_mako_templates
B703 django_mark_safe
Baseline
Bandit allows specifying the path of a baseline report to compare against using the baseline argument (i.e. -b BASELINE or --baseline BASELINE).
bandit -b BASELINE
This is useful for ignoring known vulnerabilities that you believe are non-issues (e.g. a cleartext password in a unit test). To generate a baseline report simply run Bandit with the output format set to json (only JSON-formatted files are accepted as a baseline) and output file path specified:
bandit -f json -o PATH_TO_OUTPUT_FILE
Version control integration
Use pre-commit. Once you have it installed, add this to the .pre-commit-config.yaml in your repository (be sure to update rev to point to a real git tag/revision!):
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit
rev: '' # Update me!
hooks:
- id: bandit
Then run pre-commit install and you're ready to go.
Configuration
- An optional config file may be supplied and may include:
-
- lists of tests which should or shouldn't be run
- exclude_dirs - sections of the path, that if matched, will be excluded from scanning (glob patterns supported)
- overridden plugin settings - may provide different settings for some plugins
Per Project Command Line Args
Projects may include a .bandit file that specifies command-line arguments that should be supplied for that project. The currently supported arguments are:
- targets: comma separated list of target dirs/files to run bandit on
- exclude: comma separated list of excluded paths
- skips: comma separated list of tests to skip
- tests: comma separated list of tests to run
To use this, put a .bandit file in your project's directory. For example:
[bandit]
exclude: /test
[bandit]
tests: B101,B102,B301
Exclusions
In the event that a line of code triggers a Bandit issue, but that the line has been reviewed and the issue is a false positive or acceptable for some other reason, the line can be marked with a # nosec and any results associated with it will not be reported.
For example, although this line may cause Bandit to report a potential security issue, it will not be reported:
self.process = subprocess.Popen('/bin/echo', shell=True) # nosec
Vulnerability Tests
Vulnerability tests or "plugins" are defined in files in the plugins directory.
Tests are written in Python and are autodiscovered from the plugins directory. Each test can examine one or more types of Python statements. Tests are marked with the types of Python statements they examine (for example: function call, string, import, etc).
Tests are executed by the BanditNodeVisitor object as it visits each node in the AST.
Test results are managed in the Manager and aggregated for output at the completion of a test run through the method output_result from Manager instance.
Writing Tests
- To write a test:
-
- Identify a vulnerability to build a test for, and create a new file in examples/ that contains one or more cases of that vulnerability.
- Consider the vulnerability you're testing for, mark the function with one or more of the appropriate decorators: - @checks('Call') - @checks('Import', 'ImportFrom') - @checks('Str')
- Create a new Python source file to contain your test, you can reference existing tests for examples.
- The function that you create should take a parameter "context" which is an instance of the context class you can query for information about the current element being examined. You can also get the raw AST node for more advanced use cases. Please see the context.py file for more.
- Extend your Bandit configuration file as needed to support your new test.
- Execute Bandit against the test file you defined in examples/ and ensure that it detects the vulnerability. Consider variations on how this vulnerability might present itself and extend the example file and the test function accordingly.
Extending Bandit
Bandit allows users to write and register extensions for checks and formatters. Bandit will load plugins from two entry-points:
- bandit.formatters
- bandit.plugins
Formatters need to accept 5 things:
- manager: an instance of bandit manager
- fileobj: the output file object, which may be sys.stdout
- sev_level : Filtering severity level
- conf_level: Filtering confidence level
- lines=-1: number of lines to report
Plugins tend to take advantage of the bandit.checks decorator which allows the author to register a check for a particular type of AST node. For example
@bandit.checks('Call')
def prohibit_unsafe_deserialization(context):
if 'unsafe_load' in context.call_function_name_qual:
return bandit.Issue(
severity=bandit.HIGH,
confidence=bandit.HIGH,
text="Unsafe deserialization detected."
)
To register your plugin, you have two options:
- If you're using setuptools directly, add something like the following to your
setupcall:# If you have an imaginary bson formatter in the bandit_bson module # and a function called `formatter`. entry_points={'bandit.formatters': ['bson = bandit_bson:formatter']} # Or a check for using mako templates in bandit_mako that entry_points={'bandit.plugins': ['mako = bandit_mako']} - If you're using pbr, add something like the following to your setup.cfg file:
[entry_points] bandit.formatters = bson = bandit_bson:formatter bandit.plugins = mako = bandit_mako
Contributing
Follow our Contributing file: https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md
Reporting Bugs
Bugs should be reported on github. To file a bug against Bandit, visit: https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit/issues
Show Your Style
Use our badge in your project's README!
using Markdown:
[](https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit)
using RST:
.. image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/security-bandit-yellow.svg
:target: https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit
:alt: Security Status
Under Which Version of Python Should I Install Bandit?
The answer to this question depends on the project(s) you will be running Bandit against. If your project is only compatible with Python 2.7, you should install Bandit to run under Python 2.7. If your project is only compatible with Python 3.5, then use 3.5 respectively. If your project supports both, you could run Bandit with both versions but you don't have to.
Bandit uses the ast module from Python's standard library in order to analyze your Python code. The ast module is only able to parse Python code that is valid in the version of the interpreter from which it is imported. In other words, if you try to use Python 2.7's ast module to parse code written for 3.5 that uses, for example, yield from with asyncio, then you'll have syntax errors that will prevent Bandit from working properly. Alternatively, if you are relying on 2.7's octal notation of 0777 then you'll have a syntax error if you run Bandit on 3.x.
References
Bandit docs: https://bandit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Python AST module documentation: https://docs.python.org/3/library/ast.html
Green Tree Snakes - the missing Python AST docs: https://greentreesnakes.readthedocs.org/en/latest/
Documentation of the various types of AST nodes that Bandit currently covers or could be extended to cover:https://greentreesnakes.readthedocs.org/en/latest/nodes.html
Subscribe
0 Comments
